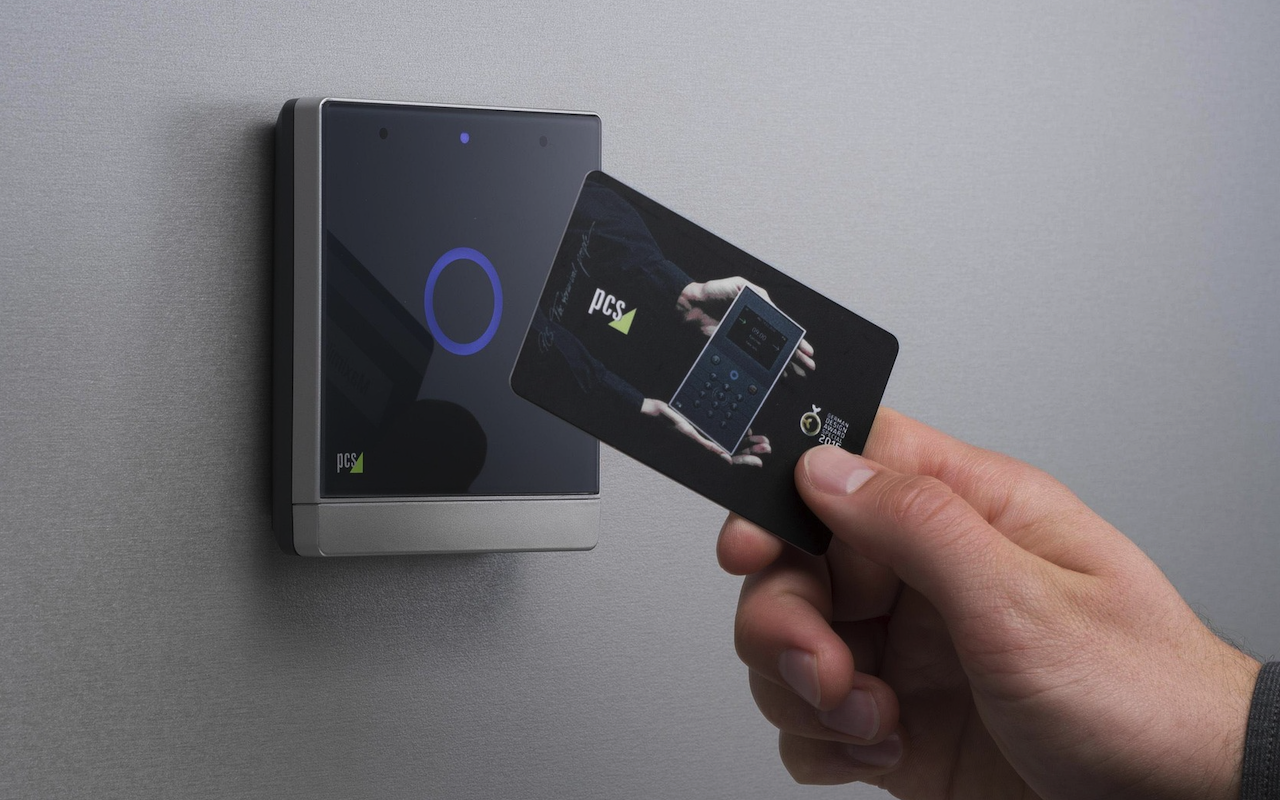

The rise of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology is changing how we interact with the world. This invisible revolution is influencing many aspects of our daily lives, from shopping to healthcare. Understanding how RFID works helps us appreciate its potential.
Understanding RFID Basics: Tags, Readers, and Antennas
Demystifying RFID Tags: Passive vs. Active Tags and Their Functionalities
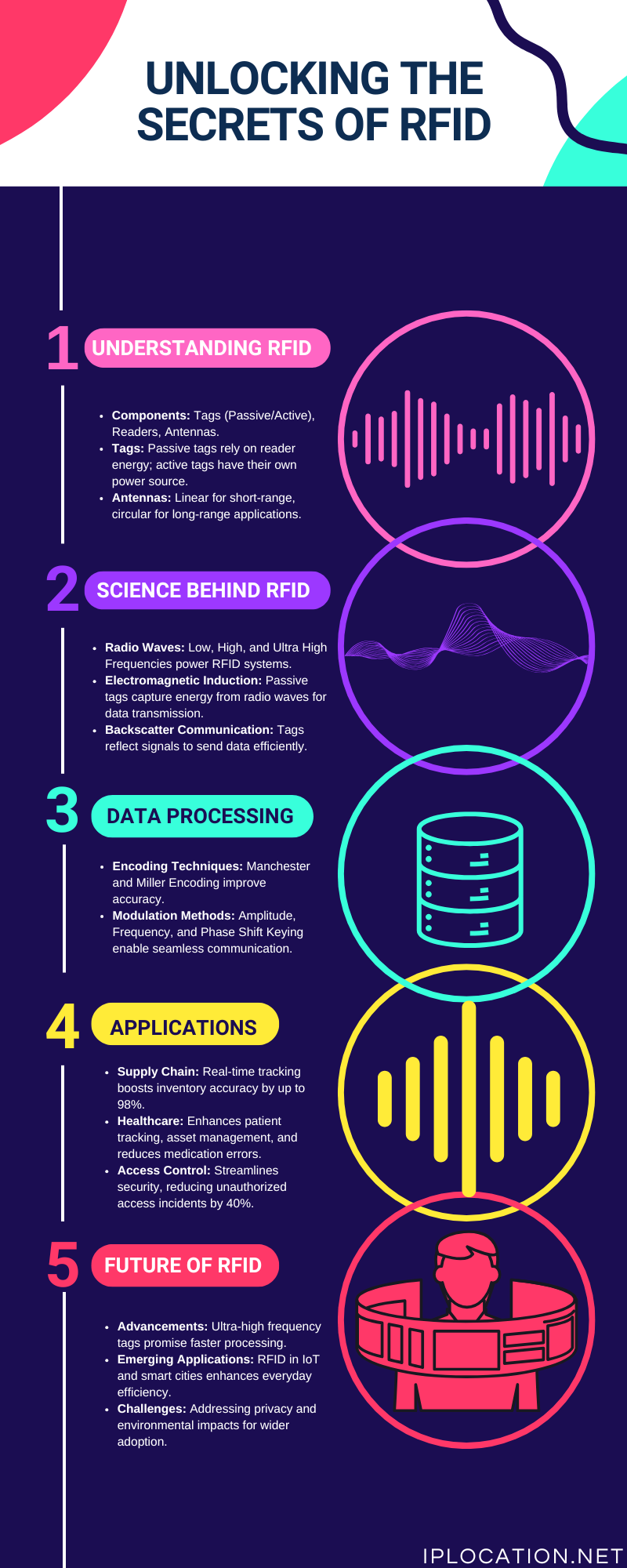
RFID systems consist of three main components: tags, readers, and antennas.
- Passive Tags: These tags do not have a power source. They rely on energy from the reader to operate. Consequently, they are smaller and less expensive but have limited range.
- Active Tags: In contrast, active tags are equipped with their own batteries. This allows them to transmit data over longer distances but makes them bulkier.
The Role of RFID Readers in Data Transmission and Communication
RFID readers serve as the bridge between tags and the system. They emit radio waves that activate the tags and read the data they contain. These readers can be handheld or fixed, depending on the application requirements.
Exploring Different Types of Antennas Used in RFID Systems
Antennas play a crucial role in the performance of RFID systems. Various types exist:
- Linear Polarized Antennas: Effective for short-range applications.
- Circular Polarized Antennas: Better for longer ranges and multiple angles of tag orientations.
The right choice of antenna affects the overall range and reliability.
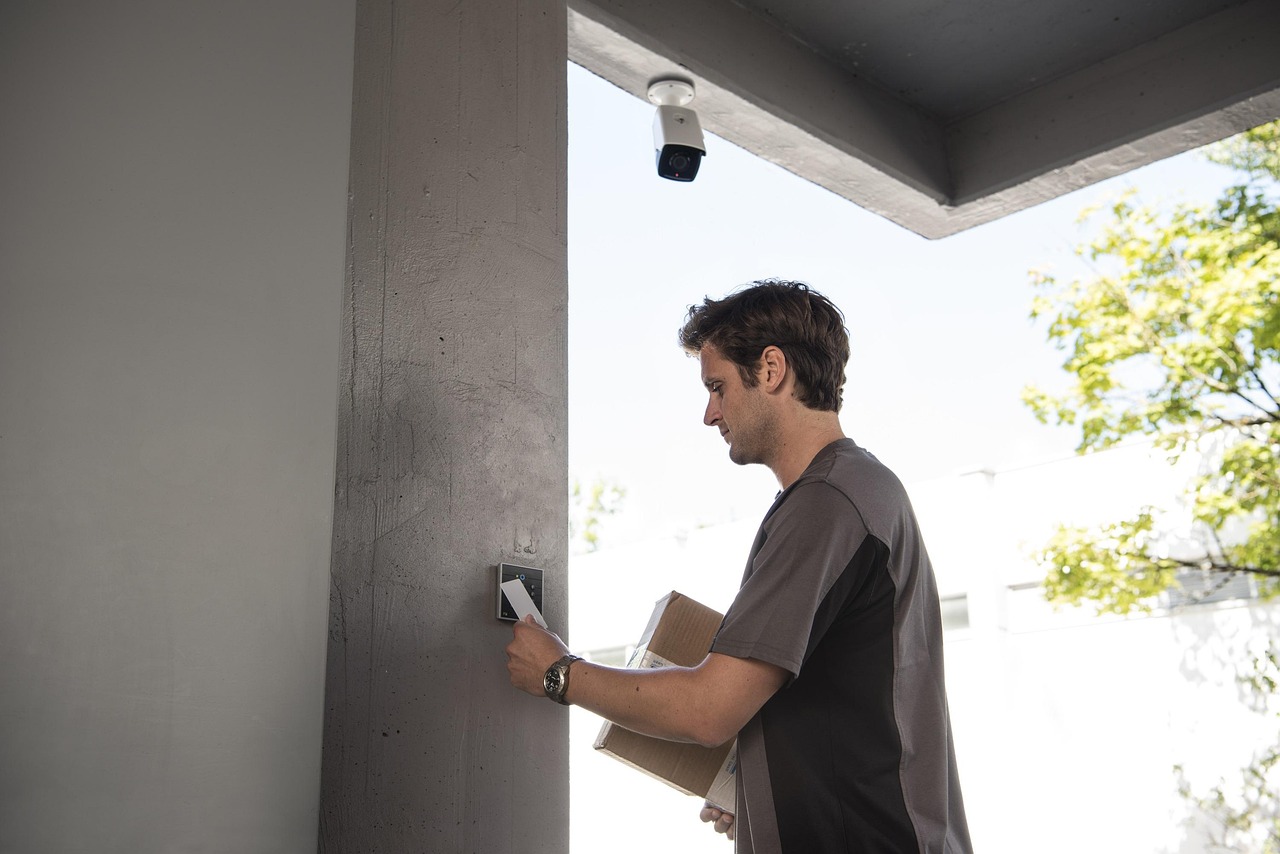

Radio Frequency Identification: The Core Technology
Deep Dive into Radio Waves and Their Properties Relevant to RFID
RFID technology utilizes radio waves to communicate. The frequencies used can range from low (125 kHz) to ultra-high (860-960 MHz). Each frequency range has its own advantages:
- Low Frequency (LF): Offers better penetration through materials but lower data transfer rates.
- High Frequency (HF): Common for short-range applications like access control.
- Ultra High Frequency (UHF): Allows longer range and faster data transfer.
Explanation of Electromagnetic Induction and Its Role in Powering Passive RFID Tags
The powering of passive RFID tags hinges on electromagnetic induction. When an RFID reader emits radio waves, the tag captures a portion of this energy. It converts it into electrical energy, which powers the tag's chip for data transmission.
The Concept of Backscatter Communication
Backscatter communication is fundamental in RFID technology. When a passive tag receives energy from the reader, it responds by reflecting the radio waves back. This allows data to be sent without needing a power source, making it efficient and effective.
Data Encoding and Modulation Techniques in RFID
Different Data Encoding Schemes Used in RFID Systems
RFID systems employ several encoding schemes to prepare information for transmission:
- Manchester Encoding: Offers a balanced transmission and reduces errors.
- Miller Encoding: Provides better efficiency, especially in noisy environments.
Exploring Various Modulation Techniques
RFID communication relies on modulation techniques, including:
- Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK): Controls signal amplitude for data representation.
- Frequency Shift Keying (FSK): Uses different frequencies to encode data.
- Phase Shift Keying (PSK): Adjusts the phase of the signal for information transmission.
The Significance of Data Security and Error Correction
Data security is crucial in RFID systems. Error correction methods help maintain the integrity of data transmission. For example, repeating the transmission can help identify and fix issues during data transfer.
Applications of RFID Technology Across Diverse Industries
Real-World Applications of RFID in Supply Chain Management
RFID technology significantly enhances supply chain processes. Statistics show that RFID adoption in logistics can improve inventory accuracy by up to 98%. By tracking items in real time, businesses save time and reduce costs.
The Use of RFID in Healthcare
In healthcare, RFID aids in patient tracking, asset management, and drug traceability. Reports indicate that RFID use in hospitals can decrease medication errors by around 30%. This technology ensures that patients receive the correct treatments on time.
RFID in Access Control and Security Systems
RFID is also prominent in access control. For example, many companies use RFID badges for employee access. These systems can increase security while streamlining entry processes. Recent surveys suggest that RFID systems can reduce unauthorized access incidents by over 40%.
The Future of RFID Technology and Emerging Trends
Discussion of Potential Advancements in RFID Technology
The future of RFID holds exciting advancements. Ultra-high frequency tags are expected to become more prevalent. These tags promise even greater range and faster data processing capabilities.
Exploration of New Applications of RFID
RFID technology is making strides into new areas, such as smart cities and the Internet of Things (IoT). Imagine traffic lights that use RFID to manage flows or smart bins that alert when they need emptying.
Addressing Potential Challenges and Limitations
Despite its benefits, RFID faces challenges. Privacy concerns arise with data tracking. Additionally, environmental factors can affect signal performance. Finding solutions to these challenges is essential for widespread adoption.
Conclusion: The Power and Potential of RFID
RFID technology revolutionizes how industries operate by enhancing efficiency and security. By understanding the science behind RFID, we can appreciate its transformative impact across various sectors. Explore this powerful technology further and consider how it might shape the future of your industry.
Share this post
Leave a comment
All comments are moderated. Spammy and bot submitted comments are deleted. Please submit the comments that are helpful to others, and we'll approve your comments. A comment that includes outbound link will only be approved if the content is relevant to the topic, and has some value to our readers.



Comments (0)
No comment