
We've learned that SSID is the network name, and we use this name to know which wireless network we're connecting to. If you've established a connection previously, your computers and smart devices have saved the password in some location for later use. Next time you need a wireless connection, the device will automatically connect to the network it has connected to before. If you can't recall the WiFi password of your router, there are ways to find the password as they are stored in your Windows, macOS, and smartphones.
Whether you use Windows, macOS, iOS, or Android, you can recover the WiFi password if you've established a connection before. We'll show you how to find your WiFi password on Windows and macOS devices. You can find the password on Android and iOS devices as well.
Windows
Whether you're on Windows or macOS, you'll be able to see all wireless networks with SSID being broadcasted. Not all wireless routers broadcast SSIDs, but they are enabled by default. The screen capture below shows available wireless networks. You'll need to know the SSID of the wireless network in order to find the password.
Windows and macOS Wireless Networks
Once you find the SSID, you can use Windows "cmd" command to find the Wifi password.
C:\> netsh wlan show profile {SSID} key=clear
The first command, "netsh wlan show profile" will show all the profiles (SSIDs) that are known to the Windows machine. The second command will provide you with the network profile of the SSID chosen, and a clear-text password. The latest Windows 10 will not reveal a clear-text password on the terminal, but all previous versions of Windows will show it.
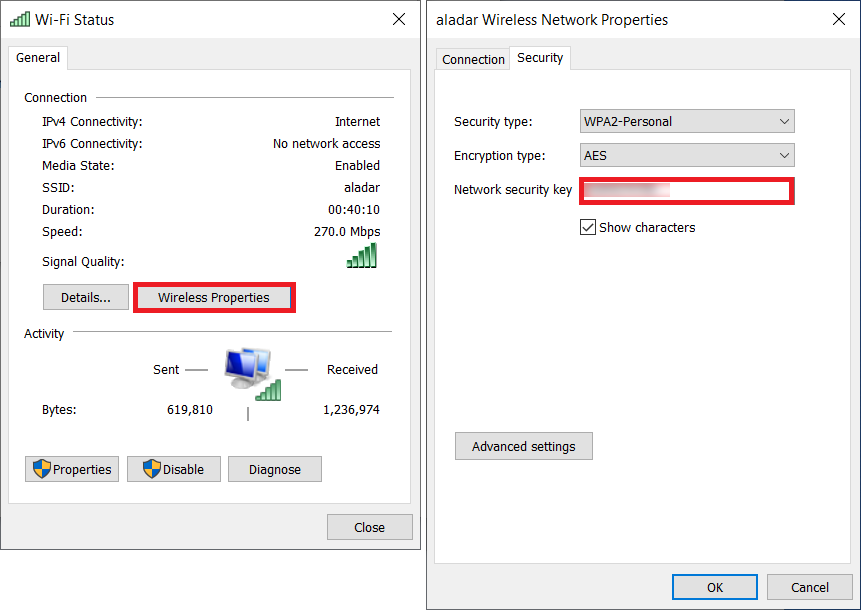
If you have Windows 10, you'll have to use graphical interface to find it's WiFi password. Click Start -> Settings -> Network & Internet -> Status -> Network and Sharing Center. On the Wireless Network Properties, click on the Security tab and you'll see the clear-text password.
macOS
On Apple devices, all passwords including WiFi password are stored in the iCloud Keychain. However, on iOS and iPadOS must sync WiFi password with the iCloud Keychain before you can view them.
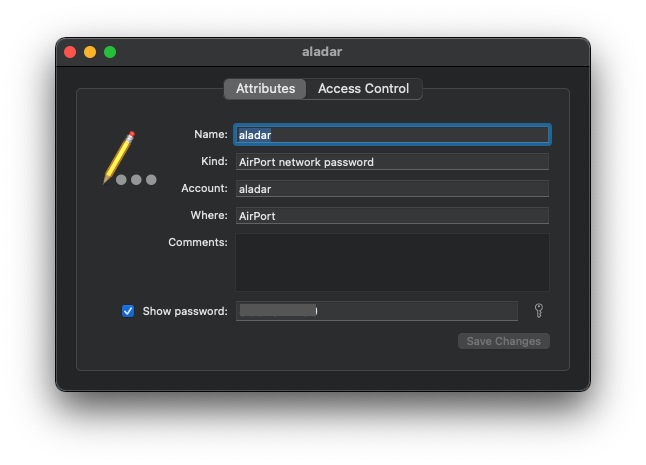
On macOS, you can use Keychain Access app to view your iCloud Keychain. Use Spotlight (Command+Space), and search for "Keychain Access" as shown below.
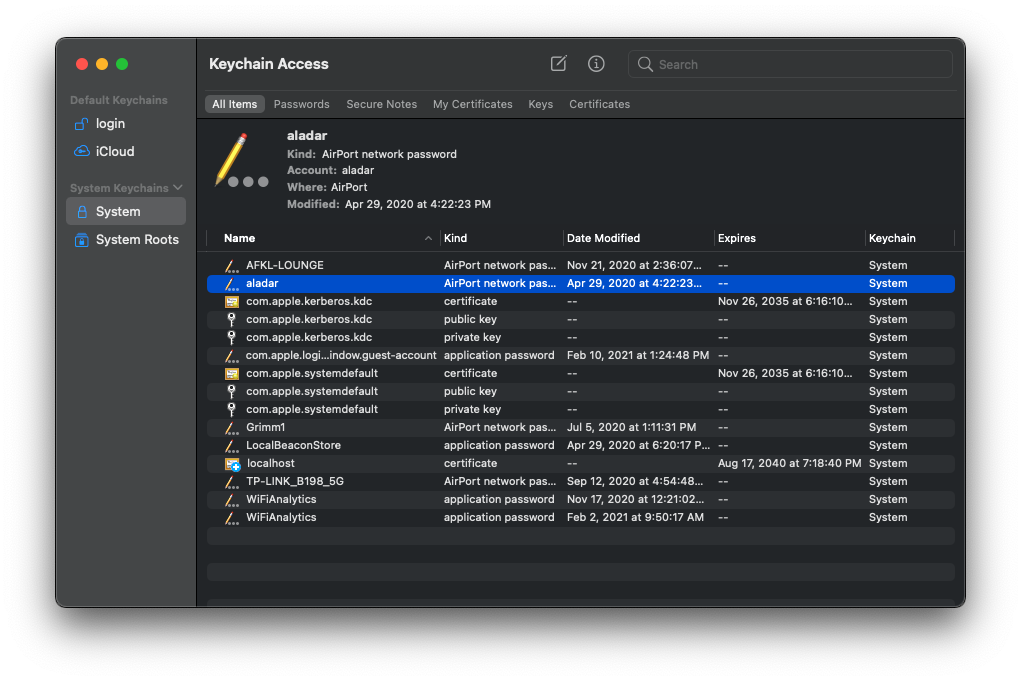
On the Keychain Access, double-click on the WiFi SSID and the dialog box below appear. Click on the "Access Control" tab, and you'll be prompted to enter your macOS username and password (twice). You'll have to enter local macOS username/password, not iCloud Keychain password.
Conclusion
On virtually any computer or smart device you use, your machine will store SSID and Password on its local storage when you first connect to the WiFi network. It uses this stored password to reconnect to the same network when you're nearby next time. You can use this stored password to reveal the clear-text password.
Share this post
Popular Articles
Email Delivery Problems Explained

November 12, 2006
With ever growing number of spam emails flooding the Internet, more and more ISPs tighten their email filtering system to prevent spams delivered to their clients. It is virtually impossible to block even 50% of the spams arriving in a mail server, and there will always be false positives (legitimate emails filte [...]
Learn moreWhat is an IP Address?

February 16, 2007
The Internet Protocol Address (or IP Address) is a unique address that computing devices such as personal computers, tablets, and smartphones use to identify themselves and communicate with other devices in the IP network. Any device connected to the IP network must have a unique IP address within the network.
Learn moreWhat is a Subnet Mask?

February 22, 2007
address and the host address. A subnet mask separates the IP address into the network and host addresses (<network><host>). Subnetting further divides the host part of an IP address into a subnet and host address (<network><subnet><host>) if additional subnetwork is needed. Use the Learn more
What is a MAC Address?

March 18, 2007
MAC, Media Access Control, address is a globally unique identifier assigned to network devices, and therefore it is often referred to as hardware or physical address. MAC addresses are 6-byte (48-bits) in length, and are written in MM:MM:MM:SS:SS:SS format. [...]
Learn moreWhat is a TCP/IP?

April 8, 2007
TCP/IP, Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol, is the suite of two protocols, TCP and IP, used to interconnect network devices on the Internet. The TCP performs the handshake between the network devices to establis [...]
Learn moreLeave a comment
All comments are moderated. Spammy and bot submitted comments are deleted. Please submit the comments that are helpful to others, and we'll approve your comments. A comment that includes outbound link will only be approved if the content is relevant to the topic, and has some value to our readers.

Comments (0)
No comment